背景
近期线上接口频繁超时, 通过日志收集工具发现, 在请求量没有大幅增加时这个接口频繁超时.
定位问题
我首先去确认了这些请求的请求内容是不是特别大.
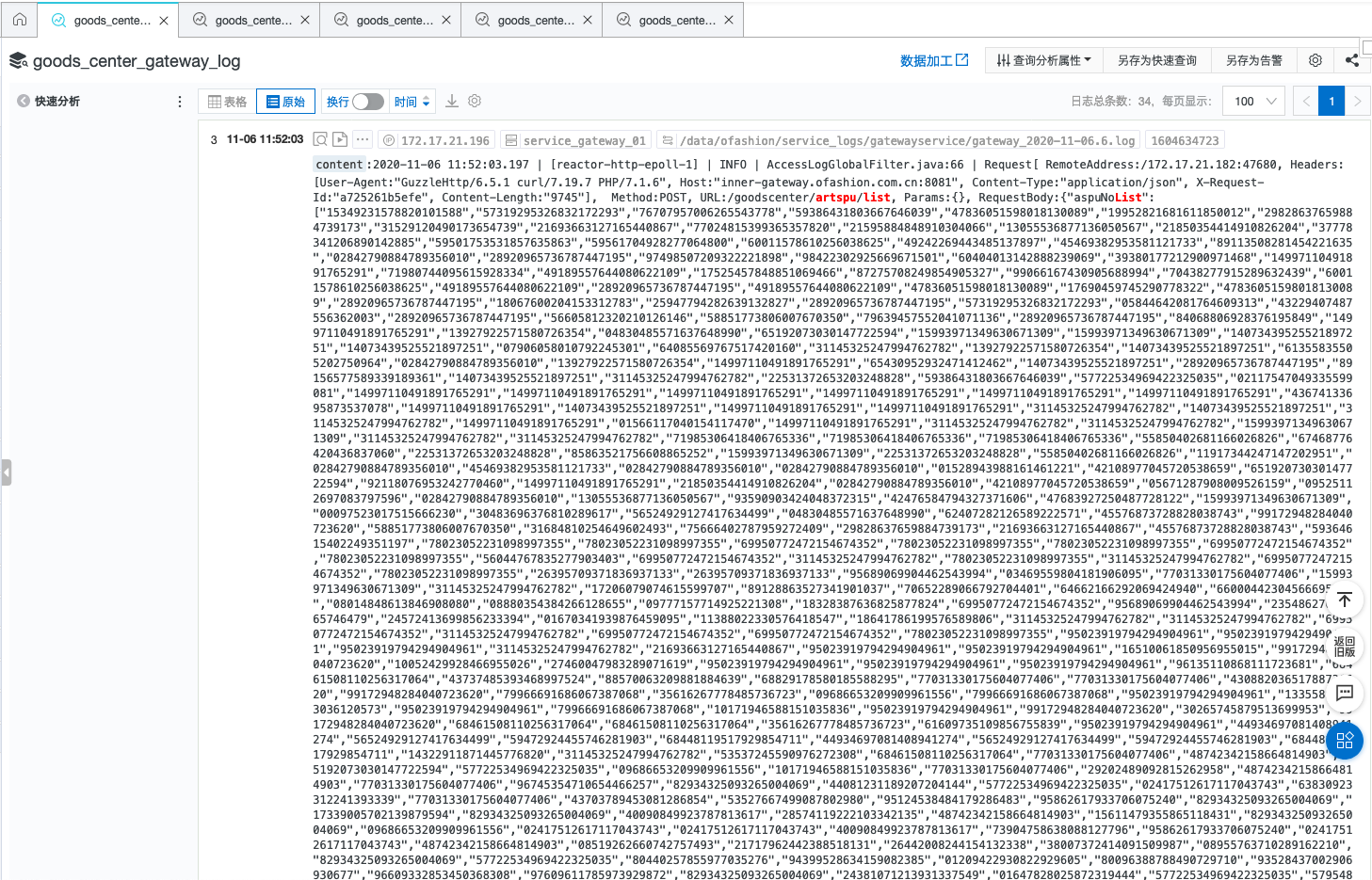
果然, 好家伙一次请求了1000多个资源, 这不慢才怪. 但是即使是请求了这么多资源也是业务的正常需求, 需要支持! 咋办? 优化呗!
使用Arthas定位耗时节点
其实我很希望能在线上环境运行Arthas, 但是由于权限不足, 申请还挺麻烦, 即是能在线上机器上运行Arthas, 我也会慌得一批, 生怕影响到应用. 所以还是选择了在测试环境操作.
启动Arthas, attach 上测试应用, 执行下面的命令
```shell script trace -n 3 -E com.ofashion.service.goodscenter.service.goods.impl.GoodsServiceImpl getGoodsInfoList ‘#cost>2000’
命令的作用是: 当 getGoodsInfoList 这个方法执行时长超过2000毫秒时则输出耗时记录, 输出3次后进行tear down
另外一边启动JMeter, 并发的请求1000个商品资源.
<img src="https://i.loli.net/2020/11/10/wJ2aHc76gbs1fOQ.png" style="zoom: 40%;" />
在Arthas控制台上能看到方法的链路耗时, 经过几轮定位后发现几个耗时严重的操作.

发现有以下几个耗时节点:
- ```RedisUtil::hMGet``` 中的反序列化
- 商品的DO与VO之间的属性拷贝
#### 优化耗时节点 - hMGet
```RedisUtil::hMGet```代码如下
```java
public <T> List<T> hMGet(Object key, Collection fields, Class<T> clazz) {
List<Object> objects = redisTemplate.opsForHash().multiGet(key, fields);
objects = objects.stream().filter(Objects::nonNull).collect(Collectors.toList());
// 这一步耗时严重
return JsonUtil.convertedToArray(JsonUtil.toJson(objects), clazz);
}
这里在处理时直接把redis客户端返回的数据序列化再反序列化为List, 处理逻辑上没什么问题
通过debug发现redis客户端返回的结构是ArrayList<LinkedTreeMap<String, Object>>
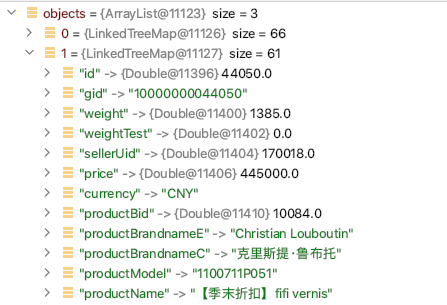
那当前这种先序列化再反序列化的方式就有些浪费资源了, 没有利用上Map的结构, 使用BeanUtil替换反序列化的这一步
得到了以下的代码.
public <T> List<T> hMGet(Object key, Collection fields, Class<T> clazz) {
List<Object> objects = redisTemplate.opsForHash().multiGet(key, fields);
return objects.stream().filter(Objects::nonNull)
.map(object -> BeanUtil.toBean(object, clazz))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
优化耗时节点 - 属性拷贝
原代码:
public void copyFrom(GoodsInfoWithExtensionDTO goodsInfo) {
BeanUtils.copyProperties(goodsInfo, this);
this.customTagIdList = CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.customTagIdList) ? null :
JsonUtil.fromJson(goodsInfo.getCustomTagIdList(), new TypeToken<List<Integer>>(){});
this.productCoverImage = StringUtils.isEmpty(goodsInfo.getProductCoverImage()) ? null :
JsonUtil.fromJson(goodsInfo.getProductCoverImage(), ImageDTO.class);
this.customImage = StringUtils.isEmpty(goodsInfo.getCustomImage()) ? null :
JsonUtil.fromJson(goodsInfo.getCustomImage(), new TypeToken<List<ImageDTO>>(){});
this.goodsImgs = StringUtils.isEmpty(goodsInfo.getGoodsImgs()) ? null :
JsonUtil.fromJson(goodsInfo.getGoodsImgs(), new TypeToken<List<ImageDTO>>(){});
this.customTags = StringUtils.isEmpty(goodsInfo.getCustomTags()) ? null :
JsonUtil.fromJson(goodsInfo.getCustomTags(), new TypeToken<List<String>>(){});
if (goodsInfo.getGoodsExtension() != null) {
this.goodsExtension = new GoodsExtensionVO();
this.goodsExtension.copyFrom(goodsInfo.getGoodsExtension());
}
}
GoodsInfoWithExtensionDTO 与 GoodsInfoVO 这两个类有很多都很多属性, 60-70个熟悉左右.
在这个基础上再并发请求1000多个资源这个耗时一下就上来了.
去搜索引擎查了一下, 没有什么理想的解决办法, 于是我回归原始, 把全部的属性拷贝都改成Setter
想想就挺折磨人的, 写这么多setter, 人不疯眼睛也花了.
还好有idea插件的支持, GenerateAllSetter

在配合上正则表达式, 生成出了全部Setter
public GoodsInfoVO(GoodsInfoWithExtensionDTO goodsInfo) {
this.id = goodsInfo.getId();
this.gid = goodsInfo.getGid();
this.weight = goodsInfo.getWeight();
this.sellerUid = goodsInfo.getSellerUid();
this.price = goodsInfo.getPrice();
this.currency = goodsInfo.getCurrency();
this.productPid = goodsInfo.getProductPid();
this.productBid = goodsInfo.getProductBid();
this.productBrandnameE = goodsInfo.getProductBrandnameE();
this.productBrandnameC = goodsInfo.getProductBrandnameC();
// 省略若干个属性的拷贝
}
验证修改的正确性
运行测试用例

OK, 这次修改没有影响软件的可观察行为, 这个方法还是可工作的.
验证修改的性能提升
本次优化的主要目的还是提升性能, 可别忘了为什么开始优化的
引入JMH测试优化前与优化后的效率提升
@BenchmarkMode(Mode.AverageTime)
@OutputTimeUnit(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
@State(Scope.Thread)
public class GoodsInfoServiceJMHTest {
private ConfigurableApplicationContext context;
private GoodsInfoService goodsInfoService;
private GoodsListQuery input10;
private GoodsListQuery input100;
private GoodsListQuery input500;
private GoodsListQuery input1000;
// 省略的SetUp 与 TearDown, 主要就是初始化上面几个变量的
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Options opt = new OptionsBuilder().include(GoodsInfoServiceJMHTest.class.getSimpleName())
.forks(0)
// 预热5次
.warmupIterations(5)
// 执行20次
.measurementIterations(20)
.build();
new Runner(opt).run();
}
@Benchmark
public void before1000() {
goodsInfoService.getGoodsBaseInfoList(input1000);
}
@Benchmark
public void after1000() {
goodsInfoService.foo(input1000);
}
@Benchmark
public void before500() {
goodsInfoService.getGoodsBaseInfoList(input500);
}
@Benchmark
public void after500() {
goodsInfoService.foo(input500);
}
@Benchmark
public void before500() {
goodsInfoService.getGoodsBaseInfoList(input500);
}
@Benchmark
public void after500() {
goodsInfoService.foo(input500);
}
@Benchmark
public void before10() {
goodsInfoService.getGoodsBaseInfoList(input10);
}
@Benchmark
public void after10() {
goodsInfoService.foo(input10);
}
}
JMH测试报告:
| Benchmark | Mode | Cnt | Score | Error | Units |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GoodsInfoServiceJMHTest.after500 | avgt | 20 | 270.904 ± 43.203 | ms/op | |
| GoodsInfoServiceJMHTest.after10 | avgt | 20 | 84.956 ± 13.687 | ms/op | |
| GoodsInfoServiceJMHTest.after1000 | avgt | 20 | 358.784 ± 150.737 | ms/op | |
| GoodsInfoServiceJMHTest.after500 | avgt | 20 | 141.310 ± 49.689 | ms/op | |
| GoodsInfoServiceJMHTest.before500 | avgt | 20 | 387.374 ± 93.433 | ms/op | |
| GoodsInfoServiceJMHTest.before10 | avgt | 20 | 125.956 ± 23.687 | ms/op | |
| GoodsInfoServiceJMHTest.before1000 | avgt | 20 | 554.784 ± 217.737 | ms/op | |
| GoodsInfoServiceJMHTest.before500 | avgt | 20 | 241.310 ± 59.689 | ms/op |
发现效率提升了大概30左右, OK降低到超时阈值以下了, 提测, 上预发布, 上线.
总结
- Arthas + JMeter 定位耗时节点
- 优化耗时节点
- 通过测试用例
- 获取JMH测试报告, 达到预期优化时间